Are you sure you know what’s causing your mastitis problems? Have you identified NAS’s?
Do you know whether you have NAS’s (Non-aureus Staphylococci) on your farm? Not yet? Remember that the better you know your enemy, the better equipped you will be to fight it, and the first step is to find out what is preventing you from achieving your targets in terms of milk quality and control of bovine mastitis. Here, we have made a few notes for you on the diagnosis and treatment of non-aureus staphylococci.
Bovine Mastitis: Best Diagnosis Methods
Once the quarters with high cell counts or that display signs of bovine clinical mastitis are detected, samples of milk should be taken aseptically and appropriately for subsequent processing in the laboratory.
Amongst others techniques, such as PCR identification, microbiology is used as a diagnostic method.
This methodology includes the usual seeding in growth media specific for the major aetiological groups.
They are incubated at 37 ºC, with readings at 24 and 48 hours. Baird Parker Agar is a culture medium specific for Staphylococci.
It makes it possible to differentiate between NAS and Staphylococcus aureus.
Non-Aureus Staphylococci usually cause mild infections and sub-clinical cases of mastitis in dairy cows.
The identification of the different species of NAS is important in order to determine their pathogenicity and to develop specific management practices to prevent mastitis.
The problem is that the identification of this group of organisms is difficult and costly. This is why many laboratories do not include species identification of NAS in routine procedures.
The identification of the different species of NAS is important in order to determine their pathogenicity
Best treatments against Non-aureus Staphylococci
It is generally assumed that the spontaneous cure rate of NAS can occur. NAS responds much better to antimicrobial therapy than Staphylococcus aureus does, and some species of NAS are susceptible to antibiotics commonly used to treat mastitis.
Treatment by intramammary therapy in the peripartum and during the drying-off period is effective for controlling infections caused by NAS. However, treatment is not always effective.
According to the National Mastitis Council (NMC), we can classify these pathogens as coagulase-negative Staphylococci sensitive to novobiocin and novobiocin-resistant coagulase-negative Staphylococci.
Some species of NAS are susceptible to antibiotics commonly used to treat mastitis but treatment is not always effective.
As we have already mentioned in a number of posts, treatment with antibiotics will soon disappear as a routine aspect of dairy farming, and European regulations and milk industry pressure will therefore force us to focus more on prevention as a cornerstone of a good management plan for bovine mastitis.
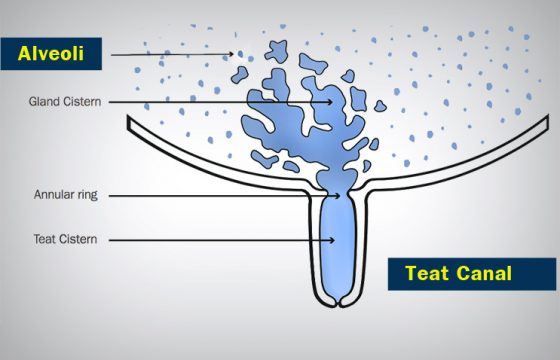
In the following post, we will focus on the prevention of this ubiquitous family of pathogens that are readily able to enter the teat canal, thereby causing bovine mastitis.
Content originally created for “STARTVAC Library No. 3”
Author: Clara Navarro Sansano.
Milk quality consultant | KERSIA/HYPRED | Spain.