Coliform mastitis: What are the main symptoms and how can you fight them?
We’ve already explained in previous posts how the cow’s immune system reacts to bovine mastitis infections and the range of vaccination options available in the market. Although we know that every disease affects the udder differently, in this entry we will examine the coliform group of pathogens in detail and we will give you some clues to reduce the impact.
Clinical mastitis: 20-40% are caused by coliforms
Despite the efforts of farmers and technicians to improve the health of herds’ udders, colibacillary bovine mastitis remains a major problem in many livestock farms.
In farms where contagious mastitis is virtually eliminated, and that have low tank cell counts, between 20 and 40% of episodes of clinical bovine mastitis are caused by coliforms.

Escherichia coli, Klebsiella spp. and to a lesser degree Enterobacter spp. are the most commonly isolated coliforms from clinical bovine mastitis episodes of this kind.
The presentation of clinical symptoms and costs stemming from them (discarded milk, treatment costs, replacement due to the death or slaughter of animals, etc.) is highly variable and depends primarily on factors in relation to the cow, rather than the pathogenicity of the strain involved.
Hyperacute coliform mastitis: What are the symptoms?
Escherichia coli, and most Gram-negative bacteria, have a characteristic and essential macromolecule in their external cell membrane called lipopolysaccharide (LPS).
This LPS is the major factor of pathogenicity of the bacterium. It triggers the typical set of symptoms of hyperacute coliform bovine mastitis.
The experimental intramammary injection of LPS in healthy animals causes the same symptoms, being dose dependent, and causes the death of the animal at high doses.
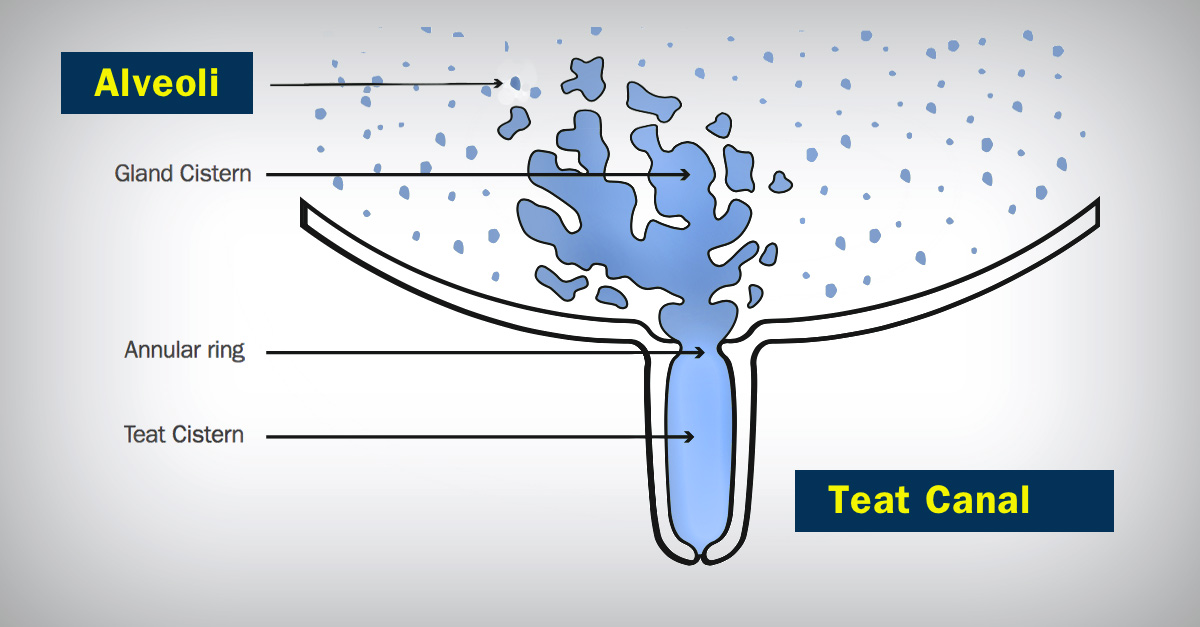
The bacterium only enters via the teat canal; it multiplies rapidly in the cistern of the udder, and in the process of multiplication and lysis, the LPS’ toxicity and potent induction of inflammatory cytokines causes generally acute symptoms in cows.
After running their course, it can cause an almost total loss of production, as well as an acute inflammation of the affected quarter and often loss of appetite, fever, listlessness, shock and sometimes death.
Depending on the immune status of the cow, the presentation may be less acute. Chronic infection with recurrent clinical episodes may also occur but that is less frequent.
Reducing the impact: The role of Neutrophils
The ability of the immune system of the cow is a key factor to limit the rapid spread of E. coli in the udder and reducing the toxic action of LPS.
Neutrophils are key players in the fight against intramammary infections. They are responsible for sequestering, killing and eliminating the pathogen.
They are aided by opsonizing antibodies, mainly IgG2 and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are responsible for the massive influx of neutrophils from the blood capillaries of the udder into the cistern.
The rapid mobilization of neutrophils into the udder is essential in reducing the impact of clinical symptoms.
In the next posts, we will discuss the predisposing factors and the recommended treatment for this type of mastitis!
Content originally created for “STARTVAC Library No. 2”.
Author: Demetrio Herrera.
Udder health and milk quality consultant | Q-Llet SLP | Spain.


