Somatic Cells & Mastitis: Tips for Interpreting SCC results correctly
As explained in previous posts, Somatic Cell Count (SCC) in milk and clinical mastitis in cattle are closely related concepts, as these tests provide with highly valuable information to prevent mastitis infections. In this post, we are going a little way further: we’ll give you some useful clues to read sampling results correctly in order to avoid any possible mistakes.
WHAT TYPE OF MILK CAN BE MEASURED?
1. Bulk milk somatic cell count (BMSCC):
A herd or bulk milk tank SCC is effectively made up of the SCCs of the individual cows contributing milk to the bulk tank at that time. It gives an estimation of how widespread infection is (prevalence) within those cows.

Although the impact an individual cow has on the BMSCC will depend on a combination of her yield and the SCC, it can be estimated that there is an increase in the prevalence of 10 per cent for every 100,000 cells/ml increase in the BMSCC. (If we see a farm with 300 SCC, we can expect to find 30% of subclinically infected animals)
However, BMSCC gives a poor indication of incidence of mastitis in cattle, as it is possible for a herd to have a low BMSCC with very high clinical mastitis rate.
Also BMSCC can be farmer manipulated by keeping milk from high SCC cows out of the bulk tank which reduces the value of the farm Bulk Milk SCC (only cows contributing to milk sold off-farm) compared to the calculated or true milk recording BMSCC (all cows in milk) which gives a more realistic picture of the udder health status of the farm.
An example of the dangers of using bulk tank SCC to monitor herd status and mastitis in cattle:
HERD 1:
100 cow herd all with SCC = 200,000
Bulk Tank SCC = 200,000
HERD 2:
92 cows with SCC = 200,000
1 cow with SCC = 2,000,000
12 cows with SCC = 1,000,000
5 cows with SCC = 500,000
Bulk Tank SCC = 250,000
Which of the two herds needs to receive treatment? The herd number 1or 2?
Number 1 all animals are below 200.000 SCC, on herd 2, on the contrary, you have 18 animals with SCC above 200.000
2. Individual Cow Somatic Cell Count (ICSCC) helps to detect mastitis in cattle:
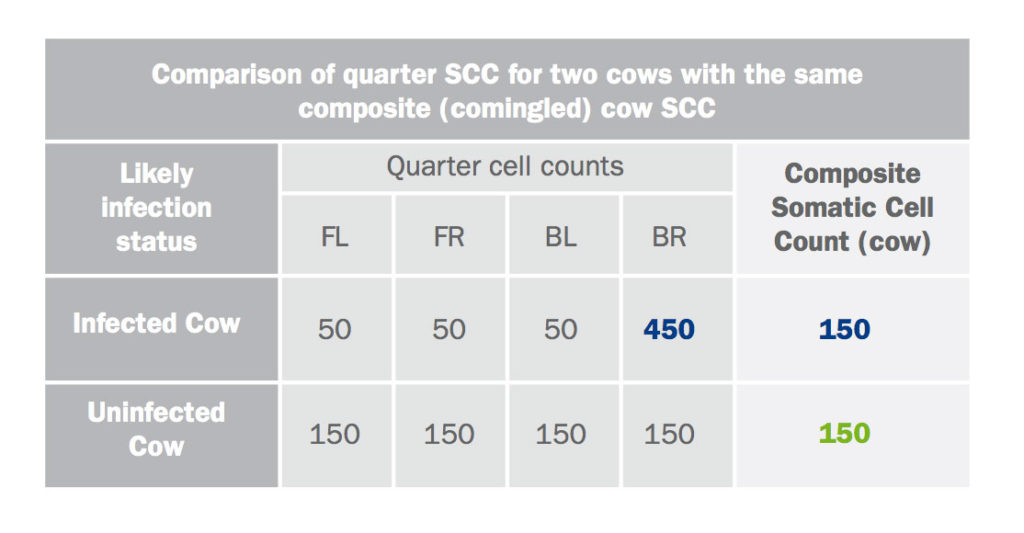
Regular monthly individual cow recording is probably the most common use of somatic cell counting and is almost exclusively performed on a composite commingled milk sample from all four quarters.
This does introduce complications in interpreting the results as it represents the average of all four quarters (assuming all quarters are of equal yield).
There is a danger that cows with infected quarters may go undetected, particularly if they have only one infected quarter with the other three having low SCCs.
Above, an example of the dangers of interpreting composite cow SCC.
Content originally created for “the Mastipedia”.
Author: Andrew Biggs, Consultant on mastitis in cattle.