Environmental versus contagious, learn how to differentiate them!
The pathogens causing mastitis can be very different, and knowing your enemy is the best way to control it. In this post we will explain the difference between environmental and contagious mastitis.
MICROORGANISM AND EPIDEMIOLOGY
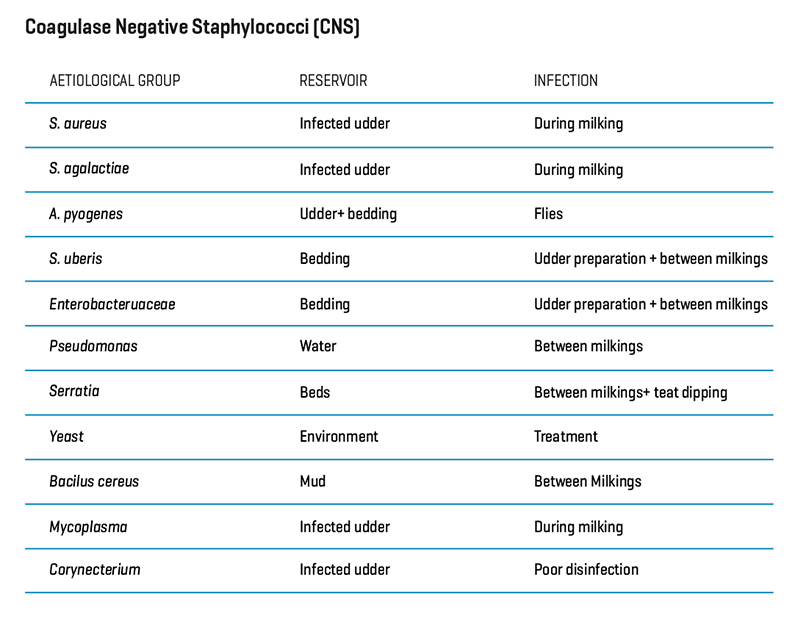
In cow’s milk we can find virus, yeast and bacteria but regarding mastitis, the most important pathogens are bacteria. The bacteria that can cause mastitis (clinical and subclinical) can be grouped in tree types: environmental, contagious and secondary (or opportunistic) pathogens. Even though this classification is the most commonly used, it is not very precise, because we know that some bacteria can act in different ways depending on the situation.
A | Contagious bacteria
This bacteria is well adapted to be able to survival and growth inside the mammary gland and are usually the responsible for chronic infected animals. Their prevalence increases as the days in milk increase. That’s because the transmission of this pathogens takes place most frequently during milking (the more milking a cow has, the more risk it’s exposed). Usually a good biosecurity management is useful to avoid the entry and spread of these bacteria.
When new animals arrive on the farm, they should be quarantined until the results confirming negativity arrive.
B | Environmental
They live in the environment, mainly in the bedding, and the infection usually happens between milkings. They replicate really quickly to survive (because they do not have tropism for the alveolar cells). They produce short duration intramammary infections and they have high clinical incidence when animals are immunosuppressed (after calving, for example). Some, such as Klebsiella, have also shown contagious behavior.
C | Pathogens with mixed characteristics
These pathogens can have contagious and environmental transmission characteristics:
D | Other pathogens that may produce mastitis occasionally
Some pathogens are less common but when present, they cause mastitis:
- Prototheca
- Nocardia
- Pasteurella
- Yeast
- Pseudomonas